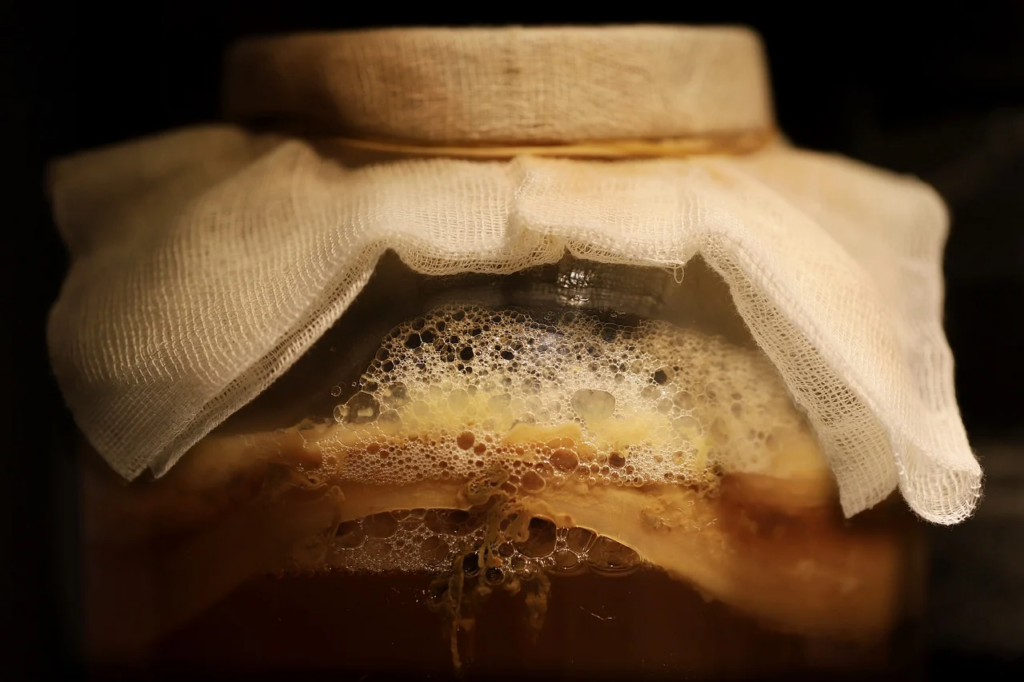

Through bacterial fermentation, these tiny organisms transform simple ingredients into an impressive range of products that improve our lives in many ways.
Think about the tangy flavor of yogurt, the fizz in kombucha, or the sharp bite of aged cheese. Each is a result of bacterial fermentation working its magic. The list goes on!
Bacterial fermentation is also central in producing renewable energy in the form of biofuels, biodegradable polymers as well as some drugs.
Let’s look at 10 intriguing bacterial fermentation products and see how these microorganisms are transforming our lives.
What Exactly is Bacterial Fermentation?
Bacterial fermentation is a metabolic process where bacteria break down sugars to generate energy in the absence of oxygen. It’s this process that leads to the production of an array of byproducts, some of which are used in food and medicine.
Where does fermentation take place? It happens in anaerobic conditions where there is no oxygen. For instance, in sealed-lid fermenting vessels.
Bacterial fermentation is a work of art used in everything from fermented foods to biofuels. Every bacterial strain and type of fermentation adds specific flavours, textures or chemical values that build up the final product.
There are entire books such as The Art of Fermentation devoted to what bacteria do in food and more. Fermentation is an old and vital process contributing to new advancements and eco-friendly solutions.
Types of Bacterial Fermentation
Several different processes are part of bacterial fermentation, each with its specific products and uses.
Let’s look at a few key types of bacterial fermentation that give us some of the most essential bacterial fermentation products.
1. Lactic acid fermentation
This procedure is driven by Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) such as Lactobacillus. These bacteria convert carbohydrates to lactic acid.
The result? The exciting sour taste we enjoy in yogurt, sauerkraut, and kimchi. But LABs aren’t just for flavor. They contribute to the natural preservation of foods, extending their shelf life without the use of chemical preservatives. Also, the bacteria are central to making fermented vegetables that are full of probiotics.
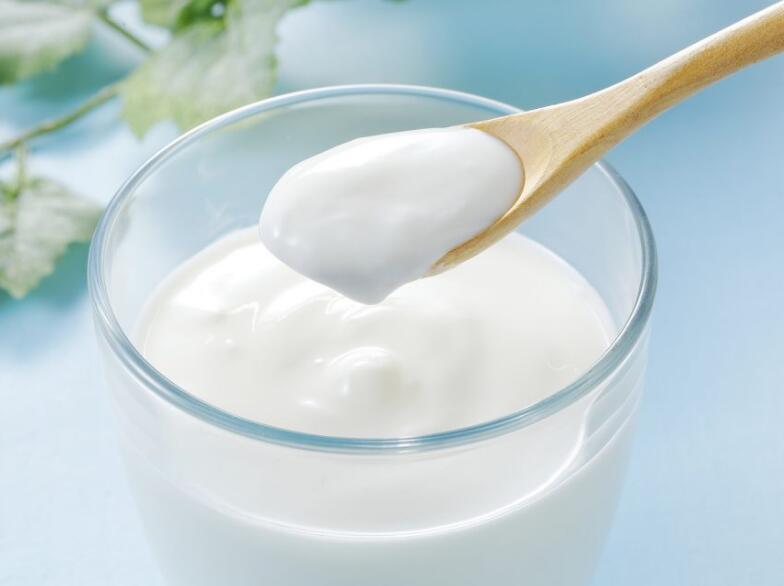

2. Alcoholic fermentation:
Although it’s often associated with yeast, certain bacteria like Zymomonas mobilis can also perform alcoholic fermentation, producing ethanol and carbon dioxide. This type of fermentation is essential in the biofuel industry, helping produce ethanol as an alternative to fossil fuels.

3. Acetic acid fermentation:
Acetic acid bacteria like Acetobacter convert ethanol into acetic acid—the main ingredient in vinegar. This not only gives vinegar its signature sour taste but also makes it a natural preservative, showing how bacterial fermentation keeps foods fresh and flavor rich.
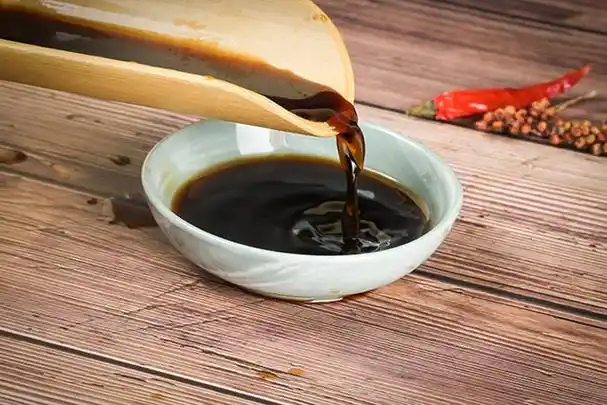

4. Butyric acid fermentation
Bacteria like Clostridium butyricum produce butyric acid in this type of fermentation. While its smell might be strong, butyric acid adds a savory, pungent flavor that makes cheese like Parmesan stand out. Now, let’s walk through ten specific bacterial fermentation products and see how they impact our lives
The 10 Bacterial Fermentation Products
1. Lactic Acid
Lactic acid is a superstar among bacterial fermentation products. Produced by Lactobacillus bacteria, it’s what gives foods like yogurt and kimchi their tangy taste.
Lactic acid bacteria fermentation is also essential in pickling and preserving foods due to its ability to create an acidic environment that prevents harmful bacteria from thriving. However, the uses of lactic acid extend far beyond food.
Applications of lactic acid
Lactic acid isn’t just for your favorite snacks. It is also used in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and bioplastics.
You’ve probably encountered lactic acid in exfoliating skin products, where it gently removes dead cells to brighten your complexion.
On a larger scale, lactic acid is used to produce biodegradable plastics, offering a more sustainable alternative to traditional materials.
Example in Food: Yogurt is a classic example where lactic acid bacteria work their magic, transforming milk into a creamy, probiotic-rich delight.
2. Ethanol
Ethanol is one of the well-known bacterial fermentation products. It is produced through alcoholic fermentation.
Zymomonas mobilis and certain lactic acid bacteria ferment sugars into ethanol. While it’s widely known as the alcohol in beverages, ethanol is also a powerful fuel source and industrial solvent.
Ethanol production is a booming industry, especially as the world seeks sustainable biofuels. In 2021 alone, ethanol production reached over 27 billion gallons worldwide as stated by the National Institute of Health.
Ethanol’s role in biofuel helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions by replacing fossil fuels.
Example in Food: You may have tasted a hint of ethanol in kombucha—fermented tea with low alcohol content produced through natural fermentation.
3. Acetic acid
Acetic acid is the main component of vinegar. It is produced by acetic acid bacteria like Acetobacter. This sour compound not only adds zest to your salads but also serves as a natural preservative.
Acetic acid helps prevent spoilage, which is why vinegar is often used in pickling and preserving foods.
Applications of acetic acid
Beyond the kitchen, acetic acid is found in cleaning products, pharmaceuticals, and the chemical industry. It’s a natural antimicrobial, making it perfect for household cleaning solutions.
Example in Food: Kombucha again showcases acetic acid at work. During its fermentation process, the ethanol produced is converted to acetic acid, giving kombucha its characteristic tangy flavor.
4. Butyric acid
Butyric acid might not sound appetizing due to its strong odor. Nonetheless, it’s a valuable product in the world of bacterial fermentation. Produced by Clostridium butyricum, butyric acid is commonly found in dairy products like cheese, contributing to its unique aroma and flavor.
Applications of butyric acid
Butyric acid is used in flavorings, perfumes, and pharmaceuticals. It adds a savory complexity to foods, especially certain types of hard cheese.
Example in Food: Parmesan cheese owes part of its distinct, pungent flavor to butyric acid produced during fermentation.
5. Propionic acid
Propionic acid is famous for its role in Swiss cheese. Produced by Propionibacterium bacteria, this compound gives Swiss cheese its nutty flavor and creates the characteristic holes within Swiss cheese.
Applications of propionic acid
Aside from cheese, propionic acid is widely used as a natural preservative in baked goods. Its antimicrobial properties help prevent mold growth, commonly found in packaged bread.
Example in Food: Swiss cheese is the ultimate showcase of propionic acid. Each hole and bite bursts with that signature nutty taste, thanks to bacterial fermentation.
6. Succinic acid
Succinic acid, produced by bacteria such as Anaerobiospirillum succiniciproducens, is one of the most versatile bacterial fermentation products. Used in everything from food additives to pharmaceuticals, succinic acid is gaining attention as a building block for biodegradable plastics.
Applications of succinic acid
Succinic acid’s applications extend to producing food flavorings, biodegradable plastics, and even as a base for certain types of medicine.
The production of succinic acid by bacterial fermentation is an area of growing research. The aim is to create cost-effective, sustainable sources for industries that rely heavily on chemicals.
Example in Food: Succinic acid adds a savory, umami flavor to products like soy sauce, highlighting its role in enhancing taste profiles.
7. Methane
Methane is a major energy source mainly released by methanogenic bacteria in anaerobic conditions. It is also produced through organic waste breakdown. Even though it isn’t directly found in food, methane generation is essential to renewable energy.
Applications of methane
Methane produced in biogas plants can illuminate homes, heat water, and even fuel cars. It is an essential component of sustainable energy solutions as it decreases landfill trash when biological waste is converted into it.
8. Hydrogen gas
Another environmentally beneficial byproduct of bacterial fermentation. Hydrogen gas is a clean fuel that burns to form water. This makes it a viable substitute for fossil fuels.
Applications of hydrogen gas
Hydrogen can be utilized in fuel cells to power tiny appliances and automobiles. The advantage of using hydrogen as a fuel is that it doesn’t contribute to air pollution. This complements the initiatives to lower carbon footprints.
9. Acetone
Clostridium acetobutylicum bacteria synthesize acetone through the acetone butanol ethanol (ABE) fermentation process. Most of us use it as nail polish remover.
Apart from domestic usage, acetone is used in the manufacturing of plastic and fibre materials, as well as in the production of drugs.
Applications of acetone
Acetone is used in industries as a solvent. It aids in the manufacturing of plastics, medicines and other products.
One potent illustration of how microbes support industrial demands is the fermentation of acetone by bacteria.
Example in Manufacturing: Acetone is important in manufacturing goods that we use daily, from medical equipment to household cleaners.
10. Biosurfactants
Biosurfactants are the natural detergents of microbial origin created by bacterial species such as Pseudomonas. These biodegradable surfactants are increasingly being adopted in the market as a replacement for conventional chemical detergents.
Applications of biosurfactants
Applicable in the formulation of surfactants in detergent. Biosurfactants are also finding applications in environmental management, particularly in the handling of oil slick. Because they are biodegradable, they are preferred by environmentally sensitive customers.
Example Application: You may find biosurfactants in some eco-friendly household cleaners.
Importance of Bacterial Fermentation Products
Think about your favorite foods—maybe it’s tangy yogurt, a savory slice of cheese, or a refreshing sip of kombucha. What all these foods have in common is bacterial fermentation.
This process doesn’t just add unique flavors and textures. It creates essential compounds that make these foods safe to eat, long-lasting, and even beneficial to our health.
Bacterial fermentation products like lactic acid and acetic acid are natural preservatives, making foods safer and shelf-stable without the need for artificial additives.
To learn more about recipes and techniques involving these products, many turn to resources like a fermented food cookbook, which offers insights into creating delicious and healthy fermented dishes at home.
However, the impact of bacterial fermentation extends beyond food. In agriculture, biosurfactants that are byproducts of bacterial activity assists the farmer in controlling soil health and minimizing the use of artificial chemicals. It is also being used in energy industries to transform organic waste into methane gas- a potent green energy that is efficient, economical and eco-friendly.
In healthcare, bacterial metabolites such as succinic acid and lactic acid are used in pharmaceuticals and supplements, thus illustrating the extent of the versatility of natural products.
Whether the goal is to enhance the flavor in the cooking, keep the foodstuffs fresh, manufacture automotive fuel, or develop medical products, bacterial fermentation products are vital to many different sectors.
Environmental and Economic Impact of Bacterial Fermentation
Bacterial fermentation is an intriguing biological phenomenon and a strong force for sustainable, economic, and environmental practices.
When it comes to waste elimination, bacterial decomposition turns the waste products into usable products, more so methane gas which is used to power homes and industries. This natural process is used everywhere in the biogas plants to convert the waste products into energy, making the world a better place.
In the food industry, bacterial fermentation decreases the use of chemical preservatives by synthesizing useful acids such as lactic and acetic acids which preserve food safety and freshness.
Bacterial fermentation is also advantageous for agriculture as biosurfactants improve the quality of soil and minimize the application of synthetic chemicals.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Though bacterial fermentation has many advantages, it also has its problems. A major challenge is contamination control, unwanted microorganisms can interfere with fermentation, lowering product quality and uniformity.
Also, the costs of production can be relatively high particularly when expanding to satisfy market demands.
With the use of genetic engineering, the future of bacterial fermentation is promising. By altering strains of bacteria, scientists can create new or valuable metabolites that have the potential to transform everything from biodegradable materials to medications.
Conclusion: The Power of Bacterial Fermentation
From tangy yoghurt to sustainable fuels, bacterial fermentation is evidence of the genius and adaptability of nature. These microscopic organisms produce goods that power our houses, fill our plates, and keep the environment clean.
We are reminded that even the tiniest organisms can have a significant impact on every bacterial fermentation product.
As we look toward a more sustainable future, bacterial fermentation is sure to be at the forefront in fueling greener industries, reducing waste, and even shaping new foods.
Next time you savour the unique flavour of a fermented treat or use an eco-friendly product, take a moment to appreciate the microscopic workers that made it possible. Bacteria may be small, but their contributions are powerful, helping us build a world that’s healthier, tastier, and more sustainable.
Power Up Your Production with BaiLun’s Pilot Scale and Industrial Fermenters
Seeking to advance bacterial fermentation? BaiLun’s Pilot scale and industrial fermenters are customized to help you scale your production needs more effectively, affordably, and accurately.
Whether you’re manufacturing food-grade items, pharmaceuticals, or biofuels, our fermenters offer the sophisticated control and capacity required for excellent outcomes.
With BaiLun, you get state-of-the-art equipment backed by years of expertise in fermentation technology. Our fermenters are crafted for durability and optimized for industrial demands, allowing you to streamline your process and maximize yield.
Ready to turn your lab results into large-scale success? Contact us today to learn how BaiLun’s Pilot Scale and Industrial Fermenters can transform your production process!
