Biosynthesis Examples in Biotechnology
The biosynthesis process is how living organisms construct for themselves those four primary compositional units that are indispensable for life and reproduction. But how does it work? How it is important in the context of biotechnology? So, what are some of the engaging biosynthesis examples that are making big impacts in fields such as; health, food production and power? Now let’s go deeper and try to find those answers.
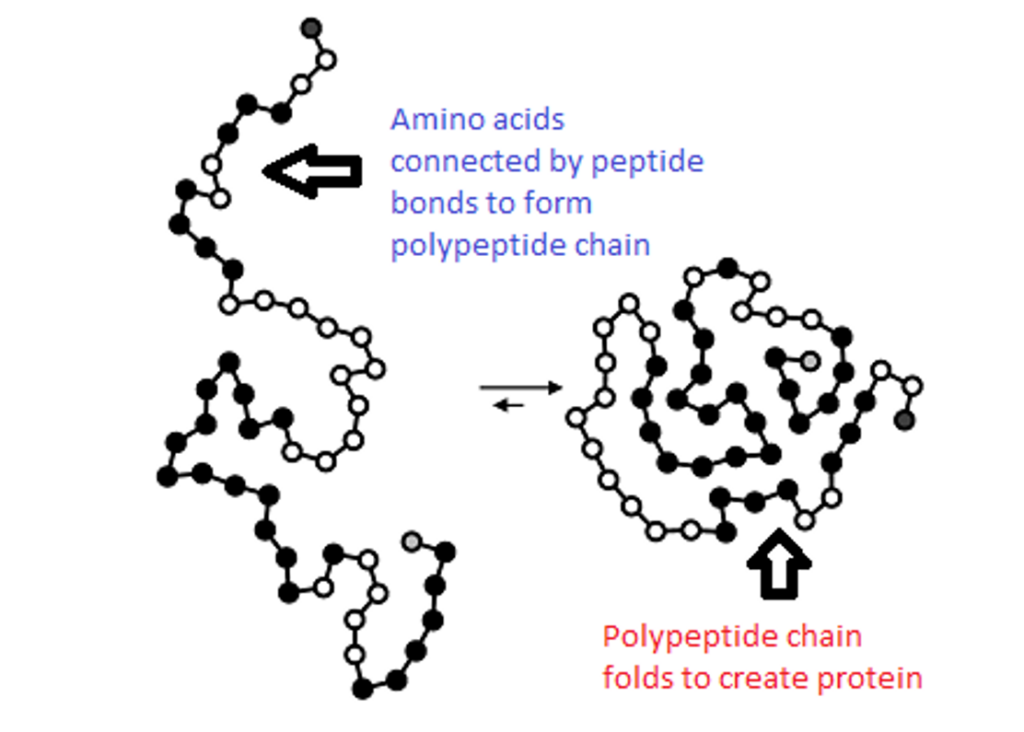
What Is Biosynthesis?
To understand the big picture, let’s first address a simple question: what is biosynthesis?
Biosynthesis means the synthesis of derivatives in an organism. Imagine it as a chemical plant, in which elementary reagents, carbon, nitrogen, and hydrogen, turn directly into such products as amino acids, nucleotides lipids and carbohydrates. Such processes occur in tightly controlled circuits thus guaranteeing that organisms synthesize what they require and in the required amounts, at the right time.
Biosynthesis is the backbone of life’s fundamental processes; from synthesizing DNA for cells to replicate or proteins necessary for its normal functioning. Biotechnology applies these processes in a manner that helps to enhance the production of medical products, and food production among other fields.
Why is biosynthesis relevant in biotechnology?
Do you want to know why biosynthesis occupies such an important place in the scientists’ interest? Let’s put it this way: without biosynthesis, there would be no antibiotics, no biofuels, no genetically modified crops and what have you. Scientists use biosynthetic routes for the synthesis of crucial medicines to green chemicals for the environment.
For example:
- One biosynthesis product which is of significant importance to diabetics is insulin a hormone synthesized by genetically engineered bacteria.
- Bioengineers employ biosynthesis examples and manufacture fuel from biological processes hence eliminating the use of fossil fuel.”
- Plants are bio-transformed genetically to produce more foods and nutrients and to defend against pests and diseases.
Indeed, biosynthesis is much more than merely a biological phenomenon; it is a technique that brings innovations.
Key Biosynthesis Pathways: Breaking It Down
Biosynthesis of Tryptophan
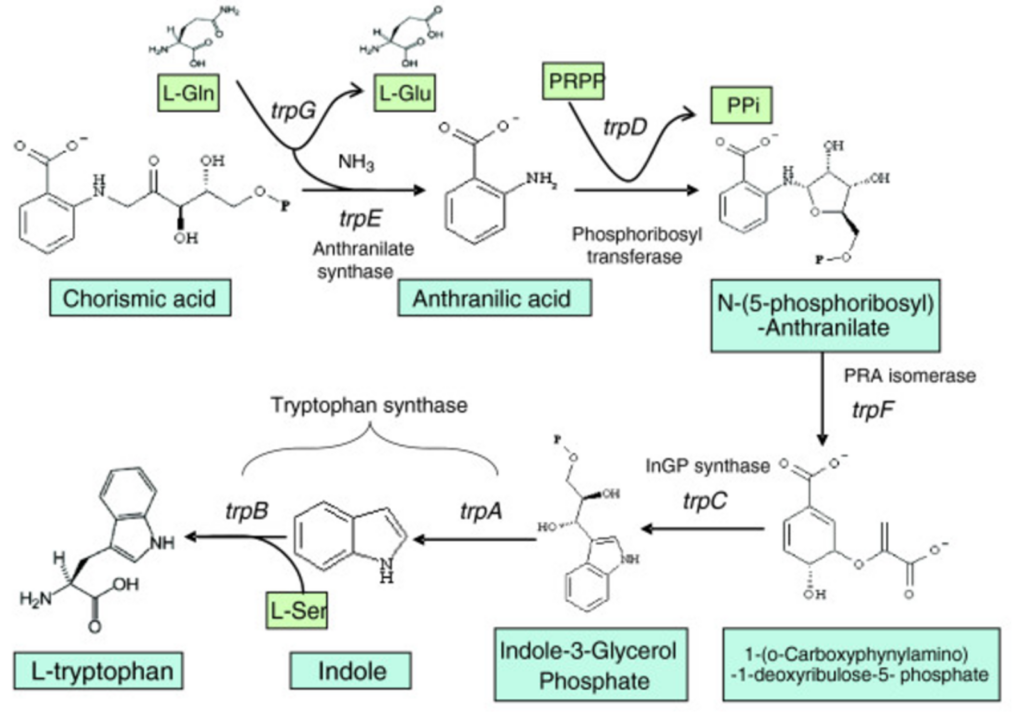
Have you ever thought about what happens when you try to synthesize the amino acid called tryptophan? It is known as the biosynthesis of Tryptophan. This indispensable molecule which prepares serotonin happiness hormone for action is a wonderful biosynthesis example.
How It Works:
Tryptophan is synthesized in microorganisms and plants by the biosynthesis process. Chorismite is the first intermediate through a number of enzymatic transformations finally yields tryptophan. These reactions are multistep making the process quite an interesting one to study.
Applications in Biotechnology:
Because of its function in the biosynthesis of serotonin, tryptophan is vital in the regulation of mood and sleep cycles. Commercial production of tryptophan utilizes microbes recruited by the biotechnologists used in dietary supplements and medicine production.
Biosynthesis of DNA
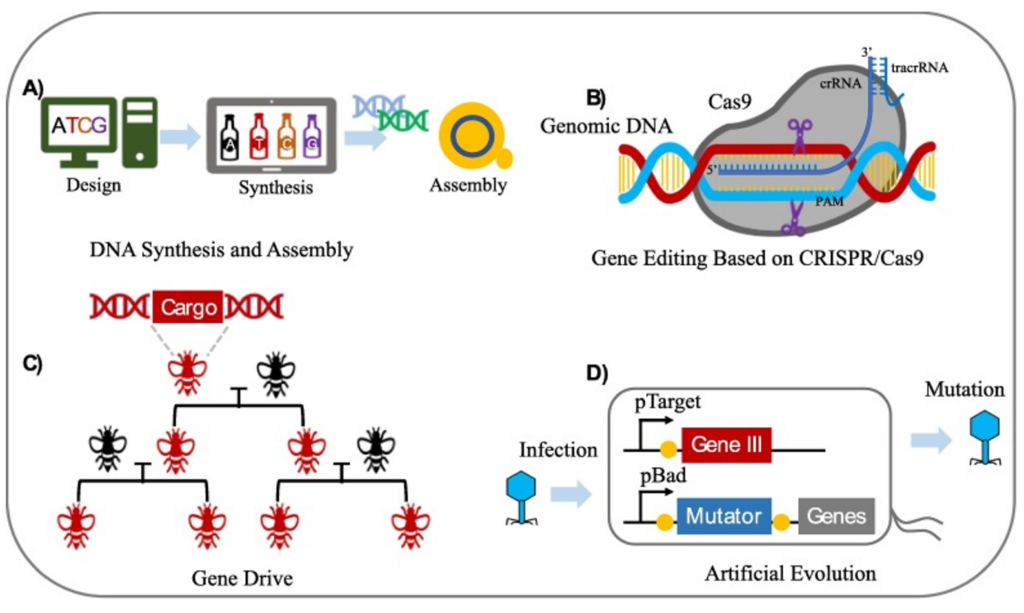
Biosynthesis of DNA plays a vital role in sustaining the life of any living organism. Without it, cells could not divide or even divide and repair themselves. But where does this process take place and why is this happening?
Where Does it Happen?
This process takes place in the cell nucleus during the biosynthesis of the DNA phase of the cell cycle. It is very controlled to maintain the correct replication of the material contained in the DNA.
Biotechnological Significance:
Biosynthesis of DNA is at the core of genetic engineering; from the development of CRISPR gene editing to the advancement of personal medicine. Synthetic DNA is applied to research genetic diseases which are conditions that affect a person’s DNA and generate completely new organisms.
3. Lipid Biosynthesis
Lipids play important roles in energy storage as well as the structure of cell membranes but how are they synthesized? The biosynthesis of lipids consists of a sequence of enzymatic reactions that take place in the manufacture of fatty acids and other lipids from acetyl-CoA.
Why It Matters:
Lipid biosynthesis is important for cell structure and energy storage within the cell. Lipid production in biotechnology is harnessed to produce biofuel medicine and other drugs.
4. Photosynthesis and carbohydrate biosynthesis
Most people do not realize that plants are extremely proficient at carrying out biosynthesis. They use sunlight in the process known as photosynthesis to produce glucose which forms the base for the formation of carbohydrates such as starch and cellulose.
Applications:
This is why scientists have latterly started research into artificial photosynthesis to produce renewable energy. Think systems are being artificially designed to catch sunlight and convert it to useful fuels!
Biosynthesis Examples
Let’s explore some more specific biosynthesis examples:
1. Antibiotic Production
Penicillin which is a family of antibiotics is produced through microbial biosynthesis. Penicillin describes the molecule that originates from the fermentation process of the mould Penicillium chrysogenum.
2. Vitamin Biosynthesis
Some vitamins for instance vitamin B12 are biosynthetically produced by microbes. These vitamins are necessary for the human body and the most popular ones that is added to other foods or found contained in pills.
3. Hormone Biosynthesis
Peptides such as insulin and growth hormones are synthesized biosynthetically for use in treatment purposes. It is now possible to design microbes to synthesize these hormones effectively without impregnating them with dangerous genes.
Challenges in Biosynthesis
Still, there are issues associated with the biosynthesis which may hinder its effectiveness. For instance:
- Cost and Efficiency: Optimizing biosynthesis processes for large-scale production purposes could be costly.
- Ethical Concerns: Should we manipulate organisms to synthesize chemicals they would not synthesize on their own? This can be a topic that is still very much up to date.
- Environmental Impact: On the same note, the industrial application of biosynthesis is always environmentally friendly.
The Future of Biosynthesis
A lot of opportunities are opening up now due to the constant developments in synthetic biology and bioinformatics. Think of microbes made artificially for synthesizing materials or plants that naturally synthesize materials that are harder than steel.
Conclusion
Biosynthesis is not something that can be studied and put aside, but the basis of life as well as the creation of new existence. Together biosynthesis of tryptophan, to the biosynthesis of DNA these pathways that are driving the future of medicine, agriculture, and energy production are here today. That is why knowledge of biosynthesis examples and their further utilization opens up solutions to many global problems. What is next to investigate in biosynthesis?
Do you derive interest in the prospect of biosynthesis in biotechnology? Whether you are thinking about becoming a researcher on this subject or just have some curiosity go through more information about this field.
Discover the state-of-the-art products moving the field forward by visiting our products at Fermenter China.
FAQs
Q1: What is biosynthesis?
Biosynthesis is the process where organisms synthesize complicated compounds from simple compounds in the structures, upkeep, and functioning of cells in the body.
Q2: Could you give some examples of biosynthesis?
Yes! Some biosynthesis examples include the biosynthesis of DNA, proteins, lipids and amino acids, specifically the biosynthesis of tryptophan which is indispensable in biological activity.
Q3: How can biosynthesis be important in biotechnology?
Biosynthesis is central to biotechnology used in generating therapeutic substances, resources for energy and genetically modified items that positively impact medical practice and sustainable sectors.
