Microorganisms Used in Fermentation
Fermentation is a key part of biotechnology since it is used in the production of food, medication and other products. But what is so special about fermentation making it possible to produce so many products globally? In essence, we’re talking about the fermentation microorganisms, might and small such as bacteria, yeast, and fungi. In this article, we will look at the amazing details of microorganisms and their impacts on different sectors.
Thus, the question arises: What is going on with bacteria and fermentation? What is the process by which fermentation bacteria produce both the tasty products we eat and the therapeutic agents we need? Without further ado, let’s go ahead and uncover the responses.\
What Do Fermentation Microorganisms Mean?
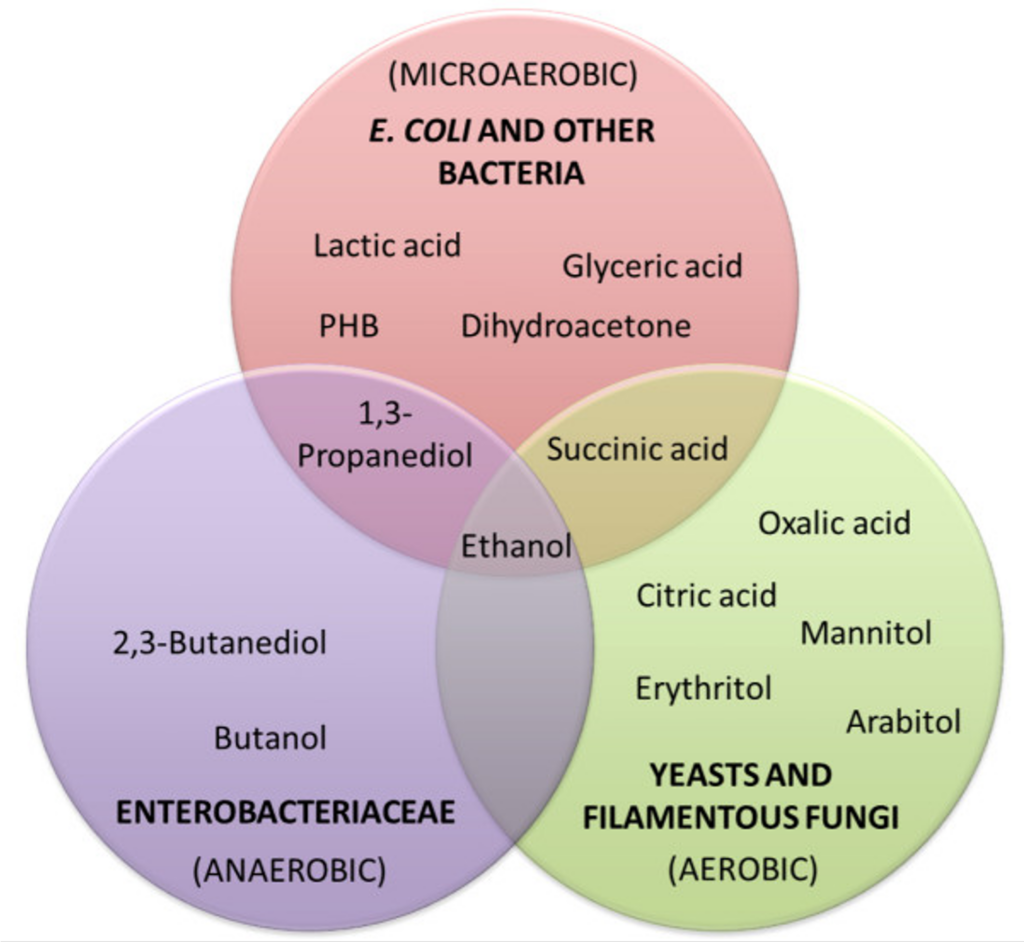
Fermentation microorganisms can be described as microorganisms that make up the fermentation process which includes bacteria, yeast and fungi. Fermentation is the process where these microorganisms convert sugars and other materials into various goods such as alcohol, acids, gases, and enzymes. This process takes place under a steady state and may be anaerobic or may occur without oxygen.
Key microorganisms
Key microorganisms include:
- Bacteria: Well established for the ability to carry out lactic acid fermentation and the production of acetic acid.
- Yeast: Used in the production of alcohol for fermentations.
- Fungi: Applied in antibacterial and organic acid production.
How Do Bacteria and Fermentation Go Hand in Hand?
If you have ever asked yourself why some foods taste sour or why antibiotics are effective, the answer is fermentation bacteria. These bacteria are of specialized type capable of metabolizing sugars into particular byproducts. For instance:
- Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB): Convert lactose to lactic acid, indispensable for making yoghurts and cheese.
- Acetobacter: These create acetic acid which is the most important ingredient in the production of vinegar.
- Propionibacterium: Produces propionic acid which imparts a unique flavor to Swiss cheese.

Examples of Fermentation Microorganisms in Action
Where do we experience the functioning of these microorganisms? Here are some common and fascinating examples:
Lactic Acid Bacteria in Dairy
- These bacteria ferment the lactose into lactic acid, the milk thickens and produces yoghurt or curd.
Yeast in alcohol Dxingzhaoarchive
- This yeast changes sugars into ethanol and carbon dioxide producing beer and wine.
Aspergillus in Soy Sauce
- This category of fungus is used to brew soybeans and wheat and give soy sauce a rich taste.
Acetobacter in Vinegar
- This bacterium uses ethanol to oxidize and produce acetic acid which is the major component of vinegar.
What Makes Fermentation Microorganisms So Essential?
It is impossible to overemphasize the importance of fermentation microorganisms. They are used everywhere from food preservation to the manufacture of medications. But why?
Food Preservation
Souring agents present in the fermentation negatively affect the nutrition-negative bacteria hence increasing the shelf period of foods.
Flavor Development
Microorganisms help to impart specific flavors and textures to host substances such as bread through kneading or fermenting and substances such as tea through brewing.
Health Benefits
Some of the specific genera of bacteria include for example lactic acid bacteria that support the gut and enhance the body’s immune system.
Industrial Applications
But their most significant application is in the production of biofuels, bioplastics, vitamins and a host of others.
What Are the Sources of Fermentation Bacteria?
To you, you might be wondering, “How do we produce these specific fermentation bacteria?” The answer, as always, is in natural selection and laboratory cultivation. Pressure is applied and specific trait adoptions are made by scientists for beneficial and safer strains in fermentation procedures.
For instance:
- Starter Cultures: Made in laboratories for the purpose of standard product outcomes such as cheese or beer.
- Wild Fermentation: Depends on the endogenous microorganisms, which are applied particularly in the context of traditional fermented products.
How Was Fermentation Discovered?
Fermentation has been in existence for thousands of years; early civilizations probably used the bacteria naturally present in the food. Much later, such luminaries as Louis Pasteur established the part played by germs, transforming food and medicine.
You would be surprised to learn that Pasteur’s work was responsible for the discovery of vaccines. This reveals how intertwined the fermentation and biotechnology industries are now that we have knitted them together on this platform.
Challenges in employing fermentation microorganisms
While the benefits are vast, there are challenges too:
- Contamination: The process can be contaminated by unwanted microorganisms.
- Strain Stability: Some become less effective within a certain period.
- Cost: Garnering a large scale from the laboratory to the industrial production involves huge capital investment.
It is therefore important that any farmer wishing to engage in fermentation should know these challenges to make better preparations for success.
How to Choose the Right Fermentation Microorganisms?
Our research focuses on one of the advisory points, that is, it is necessary to choose the appropriate microorganisms carefully if you work in the food or biotech sectors. Here’s a quick guide:
Identify the Product
- What are you fermenting; yogurt, beer or antibiotics? The microorganism is a function of the product.
Check Compatibility
- Milk must contain the specific substrate that the microorganism is capable of metabolizing, such as sugar or starch.
View Environmental Status
- In the fermentation process temperature, pH and the level of dissolved oxygen have been known to influence the rate of fermentation.
Biotechnology in the Improved Fermentation
Fermentation microorganisms have been used in very different ways by biotechnology. Modern techniques include:
- Genetic Engineering: Increases the productivity and the rate of the conversion at which microorganisms work.
- Fermenter Technology: Higher-level fermenters accommodate environmental conditions favorable for the growth of microbes.
- Metabolic Profiling: Enables scientists to be knowledgeable about, and influence, the pathways of microbes.
Conclusion
Microorganisms or microscopic creatures are often overlooked as the unsung actors behind numerous fermentation processes in food, medicine, and many industries. Whether you are eating sour cheese or getting your life-saving antibiotics, you are getting a beautiful work of fermentation microorganisms.
Feeling adventurous, and yearning for more of this exciting field? Find out how the improved technology of fermenters can change your business at Fermenter China.
FAQs
- What are fermenting microorganisms?
They cause fermentation and are bacteria, yeast or fungi that provide useful end products such as alcohol, acids or gases.
- What role do bacteria play during fermentation?
Lactic acid bacteria, acetobacter, among other types are crucial in food and flavor plus the production of vinegar.
- How do I begin with a fermentation project?
Select the correct microorganism, choose a specific product, and manage conditions on which product is used for best results.
