This article reveals these concepts, discusses their uses, and underlines their relevance in the elaborating field of biotechnology.

Inactive Synonyms and Definitions in Biotechnology
In biotechnology, inactive means substances or components that do not possess a biological activity process by themselves. For example, an inactive metabolite may be a degradation product of a pharmaceutical that no longer causes a desired pharmacological effect. In the same way, non-active components of drugs may not cure a disease but are crucial in setting up longer-lasting and effective distribution of the product.
Thus, even though the term inactive might sound like something that does not matter at all it has a significant role in the process of how certain medication is absorbed, distributed, metabolized or excreted.
Inactive vs. Active: What’s the Difference?
To understand the inactive meaning better, it’s crucial to distinguish between active and inactive components:
- Active Metabolites : They are compounds which remain pharmacologically active after a drug has undergone metabolism. They have a very direct impact on the processes of healing.
- Inactive Metabolites: Lack therapeutic activity, and therefore are eliminated by the body.
- Inactive Ingredients: Any excipients, for example, fillers, binders or stabilizers, or materials which are incorporated in the formulation of the drug to facilitate a particular objective such as the ease with which the drug can be taken or the shelf life of the preparation, but which are inactive in the treatment process.

The Role of Inactive Metabolites in Biotechnology
Metabolism is defined as the biochemical transformations that your body undergoes whenever you take medication. Commonly, these transformations bring about the formation of metabolites and they could be active or inactive metabolites.
What are Inactive Metabolites?
Inactive metabolites are the byproducts of drug metabolism that are in a position to elicit the desired therapeutic effects: Inactive metabolites are those, the strong points which are in a position to generate the necessary therapeutic effects Inactive metabolites are the byproducts of metabolite drugs that cannot produce the required therapeutic impacts. These are typically created to:
- Detoxify the body.
- Stop the functionality of the drug.
- Promote the discharge of products.
For instance, in drugs such as diazepam (Valium), the active substance is converted to active metabolite , oxazepam as well as inactive metabolites.
Why Do Drugs Form Inactive Metabolites?
Inactive metabolites are products of the metabolism of certain drugs, and the reasons behind why drugs form inactive metabolites are something we shall be answering shortly. The human body is smart and while metabolite drug , it ensures that it produces the intended results safely and in the shortest time possible. Here’s why inactive metabolites are crucial:
- Safety Mechanism: The transformation of active drugs to inactive ones is useful to prevent the drug from lingering in the body; a point which is dangerous to human health.
- Excretion Efficiency: Inactive metabolites are generally polar and can be easily metabolized and excreted either in the urine or bile.
- Controlled Effects: An example of how inactive components help the body control the time during which a drug will be effective is by creating inactive components.
Inactive Drugs and Prodrugs:
Surprisingly, not all drugs are active at the start. A significant number of drugs exist as inactive drug precursors, known as prodrugs, which generally require biotransformation before exhibiting activity.
Examples of Prodrugs
- Codeine: It is employed as an analgesic, it is a placeholder drug and is metabolized in the body by the liver into morphine, an active metabolite .
- Enalapril: This drug for hypertension is prodrug and bio-transformed in the liver to its active form, enalaprilat.
Advantages of Prodrugs
Here are some advantages of prodrugs:
- Improved Bioavailability: Some intended uses of prodrugs are aimed to increase the bioavailability of medications.
- Targeted Activation: It activates only in areas of inflammation thereby reducing adverse outcomes.
- Better Patient Experience: Prodrugs that lessen the taste or sensation of certain active drugs are present in some medicines.
The Importance of Inactive Ingredients
In the case of a certain drug, clients pay most of the attention to the active pharmaceutical’s ingredient, the substance that addresses the disease. However, inactive metabolites are just as important as active metabolites when it comes to internet marketing. Others, which may include binders, fillers and preservatives, act as stabilizers, active ingredients or ease of use.
The Importance of Inactive Ingredients
- Stabilization: Protects the active drug from degradation during storage.
- Controlled Release: To help the drug continue to be released into the bloodstream, it works to slowly release the drug.
- Improved Palatability: Improves taste or feel in the mouth, making the medication more palatable.

Applications of the Inactive Meaning in Biotechnology
The inactive meaning applies not only to the metabolism and formulation of drugs. It has various applications across biotechnology, such as:
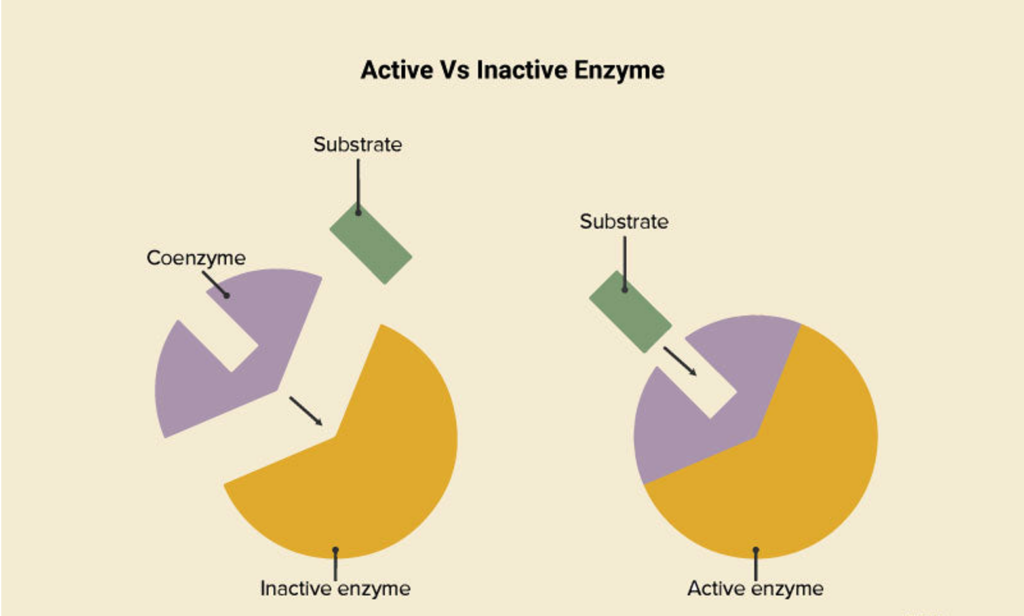
- Inactive Enzymes: Categorized as non-functional enzymes concerning mutations or environmental changes.
- Dormant Pathways: Biological mechanisms that may not be expressed in certain periods but may be expressed again under certain conditions.
- Vaccine Stabilizers: Substances in vaccines which do not contribute to the production of immunological reactants, but serve to enhance the shelf-life of the vaccines.
Can Inactive Components Be Reactivated?
Sometimes, the inactive components could get active. For instance:
- The mutated enzymes may be retrieved by the application of better gene-editing techniques such as CRISPR.
- It is possible to activate otherwise ‘inactive’ cellular functions for treatment.
This raises an intriguing question: In this way, how can biotechnology make use of the possibilities of inactivity?
Challenges with Inactive Substances
Despite their benefits, inactive components also pose challenges:
- Drug Interactions: This can result in the effectiveness of another drug being changed by an inactive metabolite.
- Allergic Reactions: Some people may have side effects from inactive ingredients such as preservatives or colors.
- Waste Management: Ridding the body of large amounts of insoluble waste products can occasionally place a burden on an organism’s systems.
Addressing These Challenges
Biotechnology has developed innovative approaches, including:
- Carrying out highly sensitive safety evaluations of inactive components.
- Developing a product with reduced proportions of inactive components: the importance of prodrugs.
- Food production to meet people’s reactions to them; the creation of special diets for individuals.
- Inactivity’s forecast for biotechnology.
The Future of Inactivity in Biotechnology
Technological developments are therefore gradually recasting inactivity in bio-technologically innovative ways. The potential applications include:
- Targeted Drug Delivery: Applying the approach of precursor molecules that are activated only in the targeted disease site.
- Synthetic Biology: Making available inactive pathways which generate useful products as well.
- Sustainable Drug Development: Avoiding harm to the environment through optimized utilization of essentially passive parts.
Just consider for a while: what if every non-interaction material could be reused for creativity? To what extent have we arrived in the ultimate world depicted in this vision?
Conclusion
The biotechnological feature of the inactive means the essential significance that inactive substances in the drug advancement and healthcare field. Starting from the biologically inactive substances which can help eliminate toxic substances from the body to the biologically inactive substances that can promote drug delivery these components make up the body of practically all the major developments in the production of drugs.
Get to know more about the field of biotechnology through the principally inactive and active metabolites and the information about the fermentations that revolutionize drugs. Contact us to shape the future of healthcare technology!
FAQs
- What role do inactive ingredients play in medications?
Excipients make sure the drugs remain stable, aid in flavoring and make manageable the rate at which the medicine can be released in the body, thus making drugs better.
- How do prodrugs work?
In other cases, the inactive drugs known as prodrugs are used in a system since they require metabolite drug processes to transform into a useful metabolite.
- Is every compound caught being dormant beneficial?
In general, inactive ingredients are not hazardous, but in some cases, certain persons may develop some sensitivity or intolerance to the particular component, say coloring or a stabilizer.
