What are Lipids ?
Lipids are one of the four fundamental biomolecules of life and can perform multiple functions in cells and the courses of human health. They are not merely energy storage molecules but also important structural units of membranes of cells and the participants of the signaling processes. Among the molecular processes of synthesis, lipid biosynthesis or lipid synthesis holds massive potential towards development in the field of medicine and industry along with research on the environment.
Guess what? Lipid biosynthesis is a far cry from lipid synthesis -yes there is a difference, and where does lipid synthesis occur in a specific location in the cell? This article guides you step by step through the process and shows what it is used for today, and why, with humor to keep you wondering through every piece of information.
Key Points of Lipids Knowledge
Lipids are insoluble in water or amphipathic organic compounds containing mainly carbon and hydrogen atoms. These are triglycerides, phospholipids, sterols and others. Lipids are critical to:
- Energy Storage: They are denser sources of energy than carbohydrates or proteins, and their store of energy is long-term.
- Cell Membrane Integrity: Phospholipids and cholesterol are involved in the formation and proper functioning of the cell membranes.
- Signaling: Lipids perform signaling functions in the metabolomics, immunomes, and reproductive systems.
It is hard to encompass in prayer what it might be like if we did not have lipids in our bodies. If these molecules weren’t present in the cells, the cells could not form well, energy storage would be a disaster, and so many important physiological processes would stop. That’s why understanding the lipid biosynthesis is fundamental to biotechnology and medicine.
Where does lipid synthesis occur ?
A common question is: Where does lipid synthesis occur? The cellular machinery responsible for lipid synthesis is highly specialized, occurring in distinct organelles:
1. Safety deposit smooth Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
The smooth ER is mainly involved in the synthesis of most phospholipids, sterols and triglycerides among other lipids.
2. Mitochondria
Although white is primarily involved in energy generation more complex cellular processes such as the synthesis of certain phospholipids like cardiolipin required for the proper function of mitochondria.
3. Plastids (in Plants)
The plastids are extremely important to plants for the synthesis of fatty acids which are precursors of many lipids.
Knowing where lipid biosynthesis takes place allows researchers to focus on certain routes of a product as well as for medical uses.
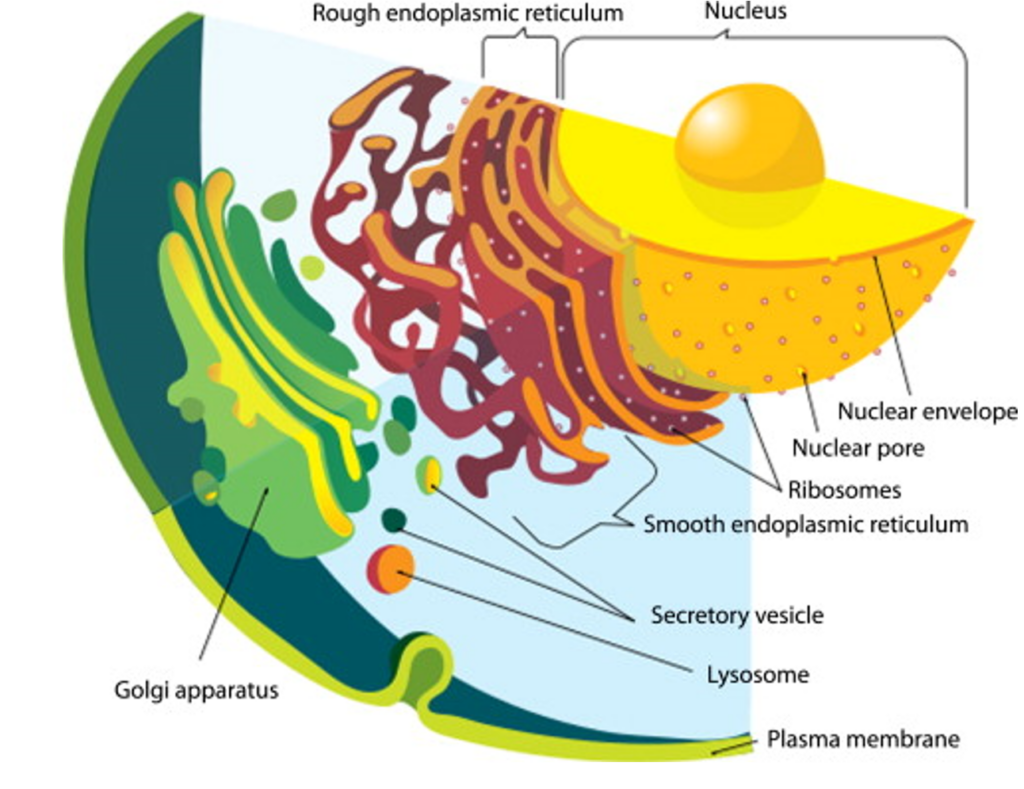
How Does Lipid Biosynthesis Work?
Biosynthesis refers to the process of lipids synthesis through a sequence of actual chemical reactions that occur in the body and are well controlled by various enzymes and pathways. Here’s an overview:
1. Fatty Acid Synthesis
- Fatty acids the main units present in most of the lipids, are mainly produced from acetyl-CoA.
- It involves enzymes such as acetyl CoA carboxylase (ACC) and fatty acid synthetase (FAS).
- The end product produced is palmitic acid which can be reacted further.
2. Glycerolipid Synthesis
- Fatty acids enter into esterification with glycerol-3-phosphate to form triglycerides and phospholipids.
- These molecules have specific roles in energy storage and the build-up of a suitable membrane to make the process worthwhile.
3. Sterol Synthesis
- Most blood cholesterol and other sterols are biosynthesized by the mevalonate pathway which is initiated by acetyl Coenzyme A.
All of these steps go on to illustrate how convoluted the process of lipid biosynthesis is and how tightly controlled this aspect of cell biology is.
When Is Lipid Biosynthesis Important?
Do you ever ask yourself why are biotechnologists so obsessed with lipids? This however lies in the fact that lipids biosynthesis has opened doors to numerous biotechnological applications.
1. Medicine
- Lipids are the main component in drug delivery systems such as liposomes as well as lipid nanoparticles.
- Lipid-based formulations for several conditions such as cancer, and cardiovascular and neurological disorders are still under investigation.
2. Renewable Energy
- New techno-ecologies of algae and microorganisms that have ideal genetic modifications to produce optimum lipid feedstocks are transforming biofuel production.
- These sustainable fuels are helping to set the tone for the greener future that is on the horizon.
3. Food and Nutrition
- Essential lipids in the food industry have better tunable characteristics that enhance texture, taste and nutrition.
- Through biotechnological developments, low-fat and trans-fat products are formulated.
- The opportunities are vast, which is why the lipids biosynthesis is the foundation of contemporary scientific achievements.
Lipid synthesis in biotechnology
Let’s delve deeper into how lipid synthesis is transforming various fields:
1. Lipid-Based Drug Delivery
In pharmaceutical technology, one of the most revolutionary applications of lipids is in the delivery of drugs. Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) help to incorporate and transport drugs and deliver them right into the target cells. For instance:
- COVID-19 Vaccines: mRNA vaccines were largely administered by LNPs.
- Cancer Therapy: Chemotherapeutic agents are currently being administered by lipid-based systems to cause lesser side effects.
2. Sustainable Biofuels
Lipids in algae are bioengineered to achieve the highest biofuel production possible. This not only causes the dependence on fossil fuels but also sets towards carbon neutrality.
3. Industrial Products
Lipids are applied in the creation of biopolymers for plastics, oils for treating machinery and foam-forming substances. The enhancement of lipid profile genetically is sustainable.
Challenges in Lipid Biosynthesis Research
Some of the difficulties hindering lipid biosynthesis investigations are as follows:
- Complex Pathways: Lipids are products of highly interlinked metabolic pathways; it is therefore difficult to control lipids synthesis .
- Environmental Sensitivity: Some factors such as temperature, pH and nutrient availability can interfere with the value chain in lipid-producing microorganisms.
- High Costs: Sophisticated technologies meaning twenty-first-century solutions like CRISPR, or large-scale proteomics employing mass spectrometry, necessitate a significant financial outlay.
The challenges highlighted above show why research in lipidomic has to go on and who should engage in this research: academia, industry and government.
The Cardiopulmonary and Lipid Perspective
The future of lipid biosynthesis holds exciting prospects:
Synthetic Biology Innovations:
Lipid technologies are nanoengineered to perform application-specific tasks in synthetic biology.
Environmental Applications:
Technologically lipids are being investigated as green substitutes for plastics and other pollutants.
Precision Lipidomic:
Future developments in lipidomic mean that patients could have treatments designed for their lipid profiles depending on a particular pattern.
These developments ensure that lipid research will continue to thrive as new discoveries are made contributing to the improvement of people’s lives.
Conclusion
Lipids biosynthesis is one of the most essential processes in living organisms and has a tremendous impact hailing from healthcare to business and technical applications as well as environmental concerns. From clean energy to smarter drugs to solving the world’s nutrition puzzle, the work being done in lipids research is changing the world.
Want to know more about these lipid-related biotechnologies? Drop by BaiLun Bio to see how these developments have come to bring a better future.
FAQ’s
- Where in cells is lipid synthesis carried out?
Fatty acid synthesis involves primarily the smooth endoplasmic reticulum with the help of mitochondria in animals and chloroplasts in plants.
- What role does lipid biosynthesis play in biotechnology?
Lipid synthesis has numerous applications in the delivery of drugs, extensive use in biofuel production, and the food industry where controlled lipids enhance nutrition and product shelf life.
- Why does lipid biosynthesis have significance?
Lipid formation is essential for cell ultrastructure, energy reserve, and cellular communications for health, longevity, transformation and technological advancement.
