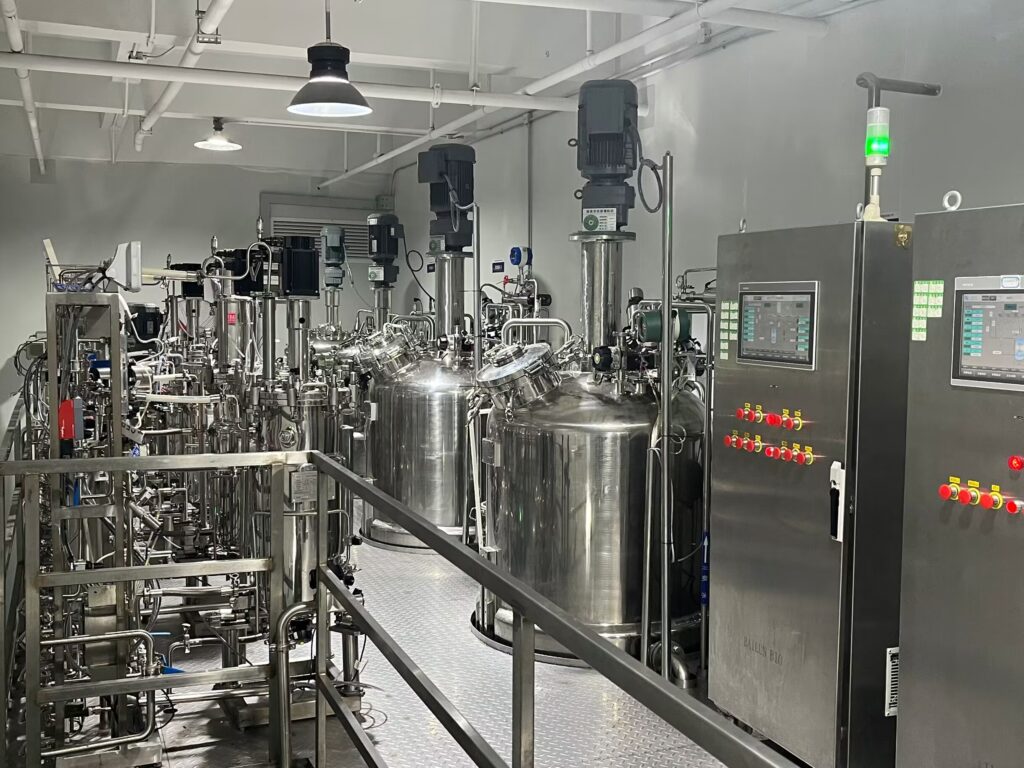
In modern industrial production, stirred tank reactors (STRs) are widely used in industries such as chemicals, pharmaceuticals, food and beverages, and biotechnology. These devices use stirring mechanisms to effectively mix reactants, accelerate the reaction rate, and ensure high efficiency and product quality. Therefore, choosing the right stirred tank reactor is critical for manufacturers as it directly impacts production efficiency, product quality, and cost control.
This article delves into the working principle, market demand, industry trends, and how manufacturers can make informed purchasing decisions based on actual needs.
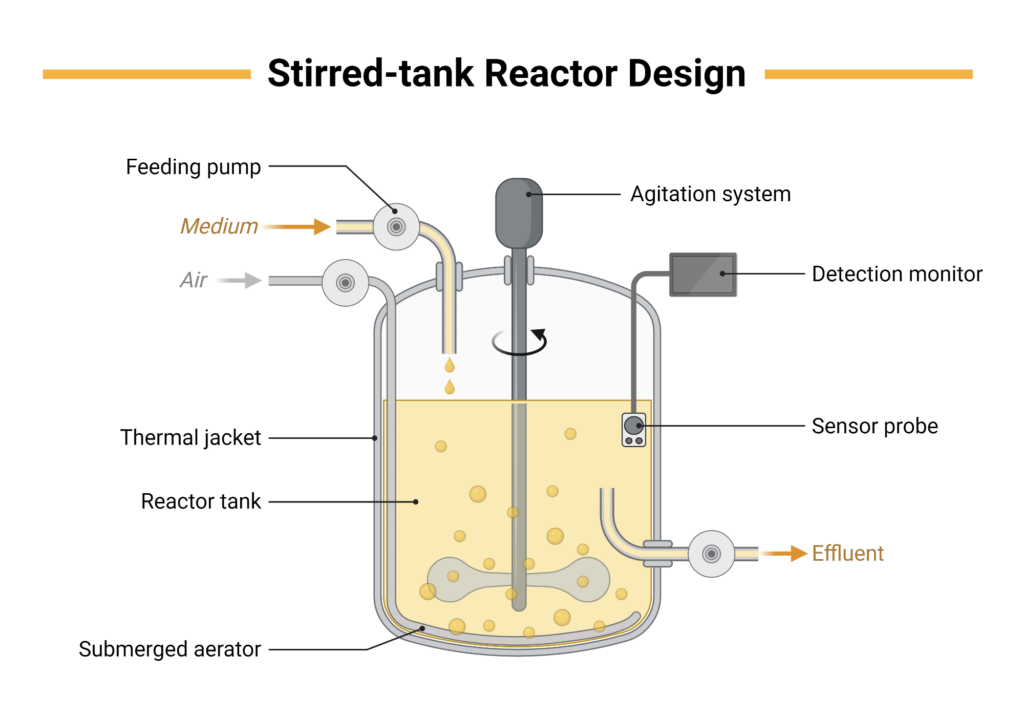
Working Principle and Structure of Stirred Tank Reactors
Working Principle
A stirred tank reactor is a common reaction device that uses mechanical or gas stirring to mix reactants evenly inside the vessel, promoting chemical reactions. Its core functions can be summarized as follows:
- Uniform Mixing of Materials: Stirring ensures that reactants are mixed quickly and evenly inside the reactor, facilitating collisions and reactions between substances, thus improving reaction efficiency.
- Heat and Mass Transfer: The reactor’s structural design ensures rapid heat and mass transfer during the reaction process, maintaining stable reaction temperatures and rates.
- Precise Control: Modern stirred tank reactors are typically equipped with automatic control systems for temperature, pressure, flow rate, etc., enabling precise adjustment of reaction conditions to achieve optimal results.
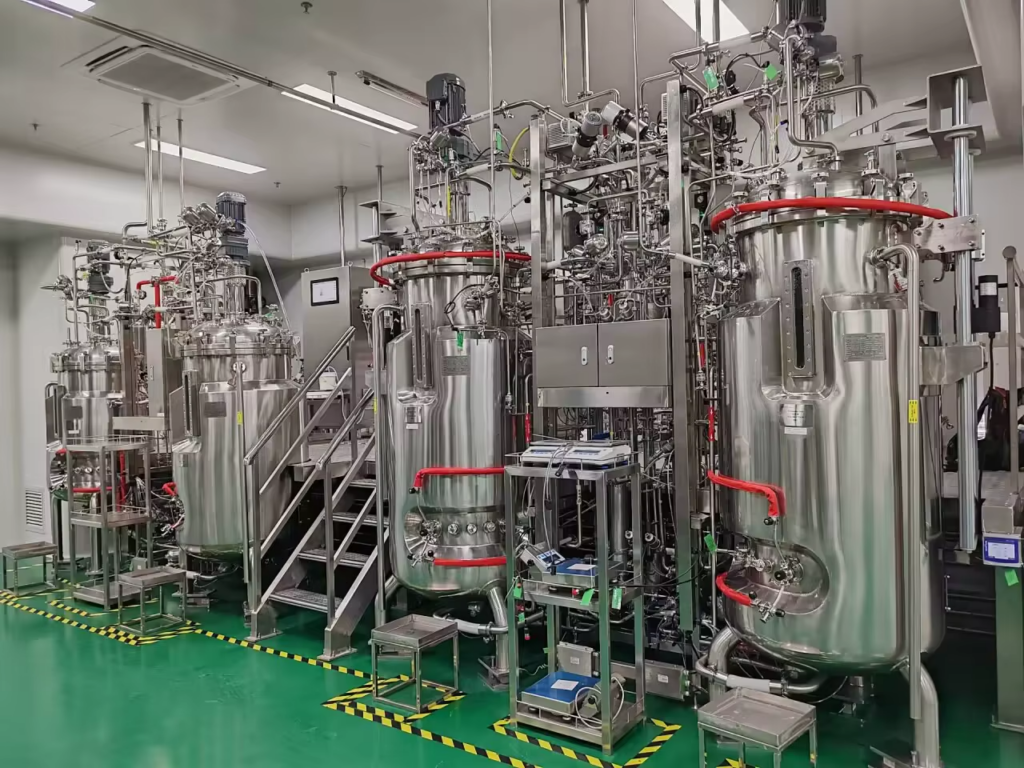

Key Components
- Reactor Vessel: Primarily used to contain reactants, often made of stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials to avoid contaminating the materials.
- Stirring System: Uses mechanical or gas stirring to thoroughly mix materials. The type and size of the stirrer depend on the properties of the reactants and production needs.
- Control System: Integrates automated systems for temperature, pressure, flow rate control, ensuring stable and controlled reactions.
- Inlet/Outlet Systems: Used for introducing raw materials and discharging products, designed to ensure the reactor’s seal and safety.
Market Demand and Industry Trends
- Automation and Smart Technology With the arrival of Industry 4.0, automation and smart technology have become core development directions for manufacturing industries. Modern stirred tank reactors are increasingly incorporating efficient automation systems, making production processes more precise and stable while reducing human intervention. For example, the integration of intelligent sensors and PLC control systems enables real-time monitoring and automatic adjustment of parameters such as temperature, pressure, and stirring speed.
For B2B clients, automated equipment not only improves production efficiency and reduces human error but also minimizes downtime and extends the equipment’s service life.
- Energy Efficiency and Environmental Protection As environmental regulations tighten, manufacturers have higher demands for energy efficiency and environmental performance. Stirred tank reactors are increasingly designed with energy efficiency and environmental protection in mind. For example, high-efficiency motors and heat recovery systems are used to improve energy utilization and reduce waste.
At the same time, gas emission control and wastewater treatment systems have become focal points for many manufacturers. Equipment suppliers continuously innovate to offer reactors that meet international environmental standards, addressing the growing market demand for sustainability.
- Highly Customized Demand With growing market diversification, customization has become a significant trend in the stirred tank reactor industry. Manufacturers desire equipment tailored to their production processes. For instance, the pharmaceutical industry requires reactors with higher cleanliness standards and precise temperature control systems, while in the chemical industry, resistance to high temperatures and corrosion is a priority.
Customized stirred tank reactors not only meet specific production requirements but also significantly improve production efficiency and ensure consistent product quality.
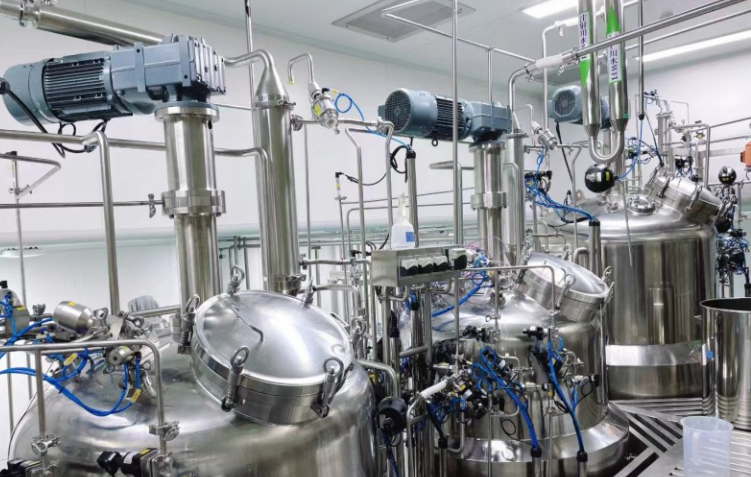

How to Choose the Right Stirred Tank Reactor
Selecting the right stirred tank reactor is a crucial decision for manufacturers. The following factors should be carefully considered in the selection process:
- Characteristics of the Reactants Different reactants impose different demands on the reactor. For example, high-viscosity materials (such as slurries, latex, etc.) require stronger stirring forces, while gas-liquid reactions (such as oxidation reactions) need appropriate gas injection systems to maintain contact between the gas and liquid phases.
- Production Scale The reactor’s volume directly relates to the scale of production. For small-scale laboratory production, a smaller reactor can provide sufficient mixing and control capabilities. In contrast, large-scale industrial production requires a larger reactor with higher stirring capacity and enhanced heat exchange systems.
- Precision of the Control System Temperature, pressure, and flow control during the reaction process are key factors affecting product quality. A highly accurate automated control system ensures stability during production and reduces manual intervention. This is especially critical in pharmaceutical and biotechnological fields, where even minor fluctuations can impact the final product quality.
- Cleaning and Maintenance Hygiene is essential in the pharmaceutical and food industries. Manufacturers should opt for stirred tank reactors that are easy to clean, particularly in cases where cross-contamination could occur during production. Many modern reactors come with self-cleaning systems to ensure thorough cleaning after each use.
- Material and Durability The materials used in the reactor must be able to withstand potential corrosion, wear, or high temperatures encountered during production. Common materials include stainless steel and alloy steels. In industries where chemical reactions are aggressive, materials with superior corrosion resistance are crucial.
How Manufacturers Can Optimize Procurement Decisions
- Define Production Needs and Budget Before selecting a stirred tank reactor, manufacturers must clarify their production processes, scale, and budget. This helps narrow down the selection range and ensures the reactor meets the company’s specific needs.
- Partner with Professional Suppliers Choosing a supplier with experience and technical support is essential. A reputable supplier can offer customized solutions based on the client’s specific needs and provide necessary after-sales service and technical support.
- Consider Long-Term Benefits While the initial investment may be higher, high-efficiency, energy-saving, and low-maintenance equipment can save manufacturers more in the long run. Therefore, procurement decisions should not only consider the price but also the long-term economic benefits of the equipment.
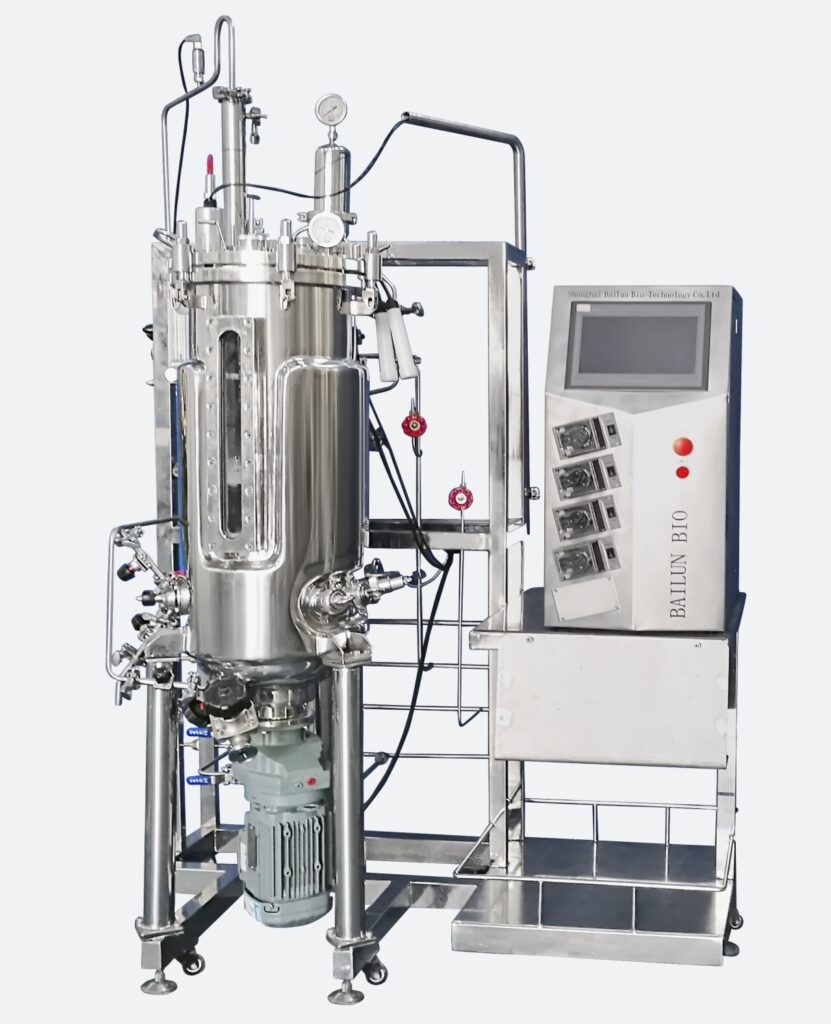

Conclusion
Stirred tank reactors are indispensable equipment in modern manufacturing. By selecting the appropriate reactor, manufacturers can effectively improve production efficiency, optimize product quality, and reduce production costs. When making a selection, manufacturers should focus on factors such as the characteristics of the reactants, production scale, control precision, and ease of cleaning and maintenance. By collaborating with professional suppliers and customizing equipment based on actual needs, manufacturers can ensure the reactors meet industry standards and align with production requirements.

