The Importance of Vaccination in Biotechnology
Vaccination is one of the greatest gifts that have been presented to human beings in this world by biotechnology. From eradicating smallpox to the epidemic control of flu, vaccines always hold a special place in future oriented health care strategies. But how, in particular, does biotechnology alter this science, which is vaccination? Which Faculty Level Responsibilities does the CDC natl immun program have and allows it to set vaccination policies? Yet, how was animal immunization helpful to our present-day vaccines?
In this article, we are to focus on the common advantages of vaccination within the field of biotechnology, comparison of the vaccinated and unvaccinated children health and general health impacts.
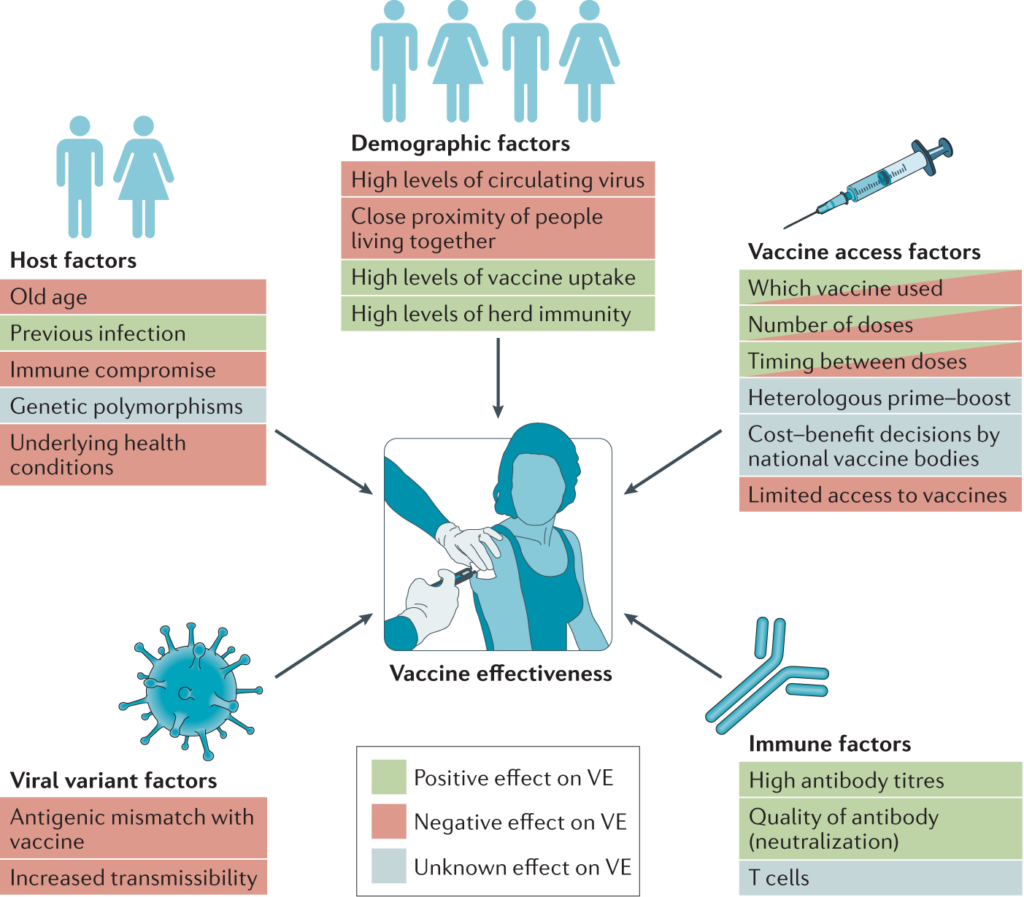
Understanding Vaccination: A Biotechnological Marvel
Vaccination is a form of preventive treatment whereby a person is administered with a substance in the pathogen such as the toxin, the pathogen that has been rendered harmless or the whole pathogen that is feeble. Nevertheless, the question that emerged here was what makes it so essential to biotechnology.
Molecular biology/Genetic engineering, therefore, results to a complete change in the kind, quality, and availability of large stocks and the least side effects in vaccines. Precisely such advancements are distributed to people all over the world in terms of immunity against deadly diseases through programs like CDC natl immun. At times the CDC natl immun change may mean adopting the case where immunity dose for a specific infection is in some way changed.
The CDC natl immun or CDC National Immunization Program has been instrumental in its work to extend vaccine use across the country. This organizational unit also focuses on the safety of vaccines, creating a work schedule, and reporting information on disease prevention.
Why Does the CDC natl immun Program Matter?
- Global Disease Prevention: It has immensely cut diseases such as polio and measles among children and youths.
- Vaccine Awareness: Issues and practices raised in public awareness enhance the knowledge of parents concerning vaccinations.
- Surveillance: The program also helps in the early identification of vaccine-preventable ailments.
Just imagine how a state can lack such a well-coordinated attempt! Seeing those preventable diseases re-emerge would be disastrous.

The Foundation of Vaccination:
Scientists previously used animals to test vaccines only before human vaccines were invented through human testing. But how was animal immunization helpful in this scenario?
1. Historical Milestones in Animal Immunization
- Edward Jenner’s Cowpox Experiment: Immunization science started in 1796 when Jenner used some agent known as cowpox to develop the smallpox vaccine.
- Pasteur’s Rabies Vaccine: Joseph Lister learned from Louis Pasteur that the vaccine was made after testing it on animals, and then vaccinating humans.
2. Key Lessons from Animal Immunization
- Understanding Immune Responses: The observations made on animals showed how pathogens behave in the immune system.
- Vaccine Safety Testing: Initial experiments for vaccine safety happened for humans.
- Development of Veterinary Vaccines: Such diseases as anthrax and Foot-and-Mouth diseases were also prevented thus defending food resources.
Without these experiments, the field of human vaccination may never have developed how it is now.
Vaccinated vs. Unvaccinated Children:
One of the controversial issues in the vaccination question is outcome data comparing vaccinated vs unvaccinated children health.
1. What Do Studies Show?
Numerous studies highlight significant differences between the two groups:
- Disease Prevention: Children, who have received their immunization vaccines, rarely develop diseases such as measles, mumps, or rubella.
- Community Immunity: Immunity achieved through the administration of vaccines keeps on defending non-vaccinated people.
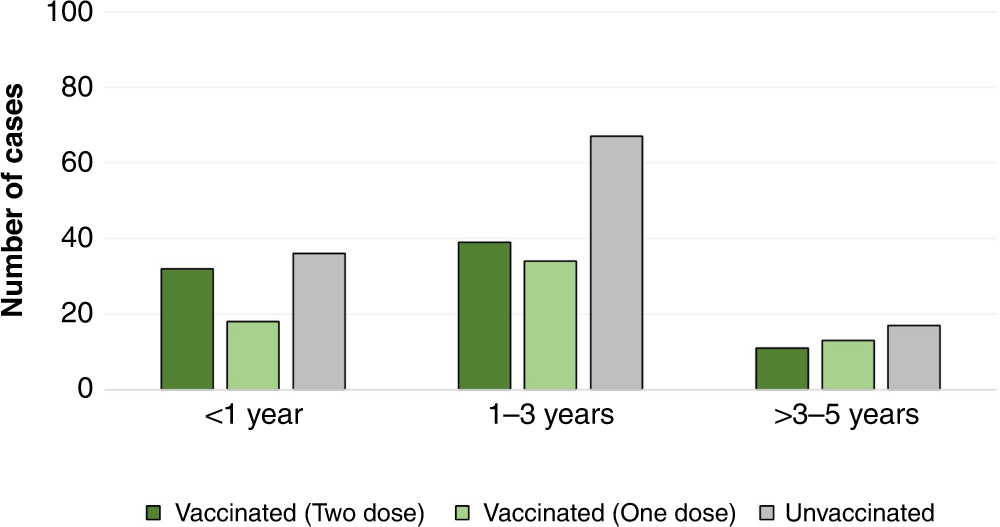
2. Risks for Unvaccinated Children
Children who are not vaccinated face higher risks of:
- Suffering from dangerous, avoidable illnesses.
- Coming down with common symptoms such as pneumonia or even encephalitis.
- Participating in causing epidemics that threaten to threaten the lives of people who are in some way or another compromised.
3. The Misconceptions About Vaccines
One of the main causes of the continued lack of vaccination is false beliefs about the vaccines. Issues of vaccine safety, however, if clarified and focused on with campaigns such as the CDC natl immun can help alleviate myths and boost confidence.
The Science Behind Vaccine Development
Vaccines are not syringes filled with a solution, they are products of state of art biotechnological engineering.
1. Types of Vaccines
Biotechnology has enabled the development of various vaccine types:
- Live-Attenuated Vaccines: Present low virulence pathogens (e.g. MMR vaccine).
- Inactivated Vaccines: They should use the killed pathogens such as the polio vaccine.
- Subunit and Recombinant Vaccines: Employ species of the pathogen; for instance, use vaccine against HPV.
- mRNA Vaccines: Introduce into cells instructions to make a harmless protein to stimulate immunity (for example COVID-19 vaccines).
2. How Do Vaccines Work?
A vaccine creates Immunological memory without actually exposing the person to the pathogen at the current high potency. Such immunological training enables the body to mount a quick yet powerful defense if exposed to the real pathogen.
How was animal immunization helpful to benefit modern vaccines?
Animal immunization can be credited for its contribution to modern vaccines. Let’s explore some examples:
- Bovine Tuberculosis Vaccine: Animal trials served as the major sources for testing human tuberculosis vaccines.
- Influenza Studies in Birds: The overall knowledge of how influenza changes in birds informed the creation of vaccines for humans.
The health of animals was then safeguarded through immunization and at the same time, the plan for saving millions of human lives was initiated.
The Role of Vaccines in Eradicating Diseases
Vaccines have achieved remarkable success in combating diseases:
- Smallpox: Eradicated globally in 1980.
- Polio: Most affected; with the cases being cut down by seventy-nine per cent since the year 1988.
- Measles: Mortality was reduced significantly down by 73% with an annual rate through vaccination between 2000 and 2018.
None of these milestones would have been feasible without intense vaccination drives backed up by CDC natl immun.
Why Are Vaccines Still Needed?
Despite these successes, vaccines remain vital because:
- Measles is an example of an illness that can come back again if people are not immunized enough.
- New diseases call for new vaccines.
- Immunization continuously makes it difficult for antibiotics to develop resistance by avoiding infections.
Killing of Germs and Dispelling Vaccine Myths
Let’s address some common misconceptions about vaccination:
1. Do Vaccines Cause Autism?
There is no scientific backup for such a statement at all. Real-life scientific research discredits a relationship between vaccines and autism.
2. How Effective Are Natural Infections Than Vaccines?
Infection with the virus, a natural infection, can lead to extremely serious complications or even death. Vaccines offer protection to the body without putting one at risk.
3. Are Vaccines Too Much for the Immune System for It to Handle?
The immune system can accept more than one vaccine at a time. Vaccines typically have low levels of antigen compared with what one is exposed to in day-to-day life.
Vaccination biotechnology
The future of vaccination is bright, with biotechnology enabling:
- Personalized Vaccines: Specifically designed to work to one’s genotype most optimally.
- Edible Vaccines: Can be packaged and distributed through such edible carriers as bananas or tomatoes, genetically modified.
- Universal Flu Vaccines: Providing longer protection against all strains of the flu virus.
- Cancer Vaccines: Using the body’s defenses to locate and eliminate cancerous tissue.
With such advancements, it is possible for the dream of eradicating even more diseases to be a reality in the not-too-distant future.
Conclusion
Vaccination had/has become perhaps the most potent biotechnological intervention because it saves millions of human lives and influences health systems around the world. Tools like CDC natl immun help ensure that vaccines get to those who need them the most, in the meantime various mechanisms of biotechnology revolutionize the immunization domain.
From knowing how was animal immunization helpful to even knowing the implications between vaccinated and unvaccinated children health, this walk-through vaccination underscored its usefulness.
Are you ready to support vaccination efforts? Discover more about vaccine production processes at BaiLun Bio and explore how cutting-edge biotechnology innovations are driving global immunization efforts. Let’s work together to create a healthier future! Contact us now!
FAQ’s
- What does CDC natl immun do?
The CDC natl immun program encourages immunizations, guards the populace against unsafe vaccines and helps avoid the incidence of vaccine-preventable illnesses.
- How does animal immunization assist in the making of the vaccines?
Animal immunization made scientists learn about immunity and test vaccines to help save millions of people through immunization from illnesses such as smallpox and rabies.
- What are the key differences between vaccinated and unvaccinated children health?
Vaccines protect children and help prevent the spread of vaccine-preventable diseases while unvaccinated children are more likely to suffer severe cases or die and help spread the diseases.
